Understanding Car Headlight Technologies: Halogen, Xenon, and LED
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to illuminating the road, car headlights have evolved significantly over the years. Today's vehicles can be equipped with halogen, xenon (HID), or LED headlight units. Each of these technologies works in a different way and has its own set of components. In this post, we break down the differences between them and explore the inner workings of these headlight systems, ideal for linking to our range of replacement parts and accessories.
Read more about, The future of automotive headlights
Halogen Headlights
How They Work
Halogen headlights have been the industry standard for decades. They function much like a traditional incandescent bulb:
Filament & Halogen Gas: At the heart of a halogen bulb is a tungsten filament that heats up when electricity is applied. The bulb's glass envelope is filled with a halogen gas (usually iodine or bromine), which helps redeposit evaporated tungsten back onto the filament. This process not only improves the light output but also extends the bulb's life. Some performance halogen bulbs can also be filled with Xenon gas, these have a slight improvement over standard halogen bulbs but they mustn't be confused with a Xenon HID Bulb which is different.
Heat & Light Production: As the filament heats, it emits a warm, yellowish light that is directed by the reflector.
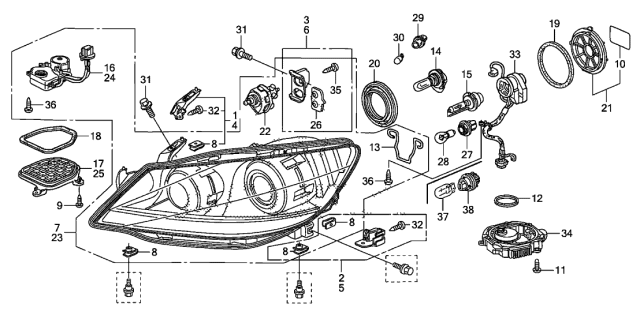
Key Components for Halogen Units
Halogen Bulb: The light source that is filled with gas that heats up the filament to produce light.
Levelling Motor: Used to either raise or lower the headlight beam manually from within the car by the driver.
Reflector or Projector Lens: These shape and focus the light beam to optimize road illumination, Originally all halogen lamps had a reflector lens, these are quite poor at producing a good beam pattern and efficiently emitting the light out of the headlight. Projector Lens are fairly new technology and do a much better job at producing perfect beam patterns and emit the light much further than a reflector style headlight.
Xenon HID Headlights
How They Work
Xenon headlights, often referred to as High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, differ fundamentally from halogen:
Gas Discharge Process: Instead of a filament, xenon units use a pair of electrodes inside a quartz or ceramic housing. When a high voltage is applied, the xenon gas (often mixed with argon and metal salts) is ionized, creating a brilliant, white light.
Ballast Requirement: Because the ionization process requires a controlled surge of electricity (24Kv), xenon systems include a ballast that regulates the power supply, ensuring consistent performance.
Key Components for Xenon Units
Xenon HID Bulbs: A xenon HID bulb is a high-intensity discharge lamp that produces light by creating an electric arc between tungsten electrodes in a chamber filled with xenon gas & mixed with metallic salts. It is the salts that determine the colour output of the light. (5000k - White, 6000k - Ice White, 8000k - Blue)
Xenon HID Igniter: Some xenon bulbs used to have the ignitor separate to the bulb itself. These are used to fire up the xenon bulb once the arc is established the ballast takes over. Some bulbs that require an ignitor are D2R, D2S & D4S. D1S, D3S D8S & D5S all have the ignitor built in.
Xenon HID Ballast: An electronic unit connected to the Xenon HID Bulb that provides the correct voltage and regulates the power, ensuring a stable discharge. Without a ballast, the Xenon Bulb cannot function at all.
Levelling Motor: Modern headlamp levelling systems—often integrated as part of an adaptive front-lighting system (AFS)—employ sensors (typically mounted on the vehicle's suspension) to continuously monitor changes in ride height or pitch. For example, when a heavily loaded vehicle causes the rear to sag, the sensors detect the change in vehicle inclination. A control module then commands small actuators or levelling motors on each headlamp to lower the beam to the correct angle. This real-time adjustment ensures that the beam remains properly aligned and reduces glare to oncoming vehicles.
Headlight Cleaning Systems: Headlight washer systems on xenon HID headlights are integrated cleaning mechanisms designed to keep the headlamp lens pristine. Because xenon HID bulbs produce a very intense, focused beam, any dirt, insect remains, or grime on the lens can scatter the light, leading to reduced performance and increased glare for other road users.
These systems typically consist of:
- A fluid reservoir and pump: Supplies cleaning solution under pressure, normally from the same reservoir as your windscreen wiper fluid.
- Nozzles or jets: Direct the spray precisely onto the lens surface, these are often controlled by a actuator and only come out of the bumper when cleaning your windscreen whilst your lights are turned on.
- Wiper Blades: Some vehicles also have wiper blades that physically wipe the dirt from the headlight lens.
Check out our range of Xenon Bulbs and Ballast Systems to restore your vehicle's headlight performance.
Read more about, Upgrading Xenon HID Bulbs to LED, Different Types of Xenon HID Bulbs
LED Headlights
How They Work
LED headlights represent the forefront of automotive lighting technology. Instead of using a filament or gas discharge, LED systems generate light through semiconductor chips. When electricity flows through these LED chips, they emit photons in a highly efficient manner, producing a bright, crisp, and energy-saving light output.
Key Components of LED Headlight Systems
Modern LED headlight units are not just a single bulb—they are sophisticated systems made up of several distinct modules, each serving a specific purpose:
LED Headlight Module: This is the primary module that controls the array of LED chips responsible for the dipped or main beam. Its design allows for precise control of the light output and beam pattern, ensuring optimal illumination of the road.
AFS Cornering Module: The Adaptive Front-lighting System (AFS) Cornering Module adjusts the direction of the light beam based on the vehicle's steering and speed. It enhances safety by illuminating road curves more effectively, ensuring that the driver has better visibility during cornering.
LED Indicator Module: This module is used to control the LED turn signals and other indicator functions. It ensures that the signals are bright and visible while maintaining a seamless integration with the headlamp design.
LED DRL Module: The Daytime Running Light (DRL) Module is designed to operate as a low-power, continuous light during daylight hours. It provides enhanced visibility to other road users without causing glare, contributing to overall vehicle safety.
Additional Considerations
Because LED systems are sensitive to temperature and electrical current fluctuations, they include:
LED Drivers: These electronic components regulate the power supplied to the LEDs, ensuring a consistent light output and protecting the LEDs from electrical surges.
Heat Sinks: Integrated into the module design, heat sinks dissipate any excess heat generated by the LED chips, prolonging the lifespan of the module.
Optical Lenses and Reflectors: These components shape and focus the light beam, allowing for advanced beam patterns and adaptive functions such as glare control and dynamic lighting.
Read more about, AFS Cornering Modules
Comparing the Technologies
| Feature | Halogen | Xenon (HID) | LED |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Source | Tungsten filament | Ionized xenon gas & electrodes | LED chips |
| Light Color | Warm yellow | Bright white/blue-white | Crisp, white light |
| Lifespan | 200–400 hours | 2,500–10,000 hours | 10,000–30,000 hours |
| Power Consumption | Higher wattage | More efficient than halogen | Most energy efficient |
| Components to Replace | Bulb, levelling motor. | Xenon bulb, ballast, igniter. levelling motor, washer pump. | LED chips (rarely), headlight module, afs module, indicator module, drl module. |
Each system has its benefits. Halogen units are simple and affordable, xenon units provide a brighter and more striking beam, and LED units offer energy efficiency and design flexibility. However, knowing the internal components of each headlight unit is crucial especially when it comes to replacing parts or upgrading your system. This insight can help you choose the right components from our product range.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're looking to replace a halogen bulb, upgrade to a xenon system, or invest in modern LED technology, understanding the differences—and the parts inside each headlight unit—ensures that you can make an informed decision. With our wide selection of high-quality replacement parts, you can find everything you need to keep your vehicle's lighting system safe and efficient.
Explore More
Explore our full collection of headlight components and replacement parts to find the perfect fit for your car.
